Identifications - Cold War (chapter 32):
Tehran, Yalta, and Potsdam Conferences (overview) - last week - thanks Andrew (from other section)!
- Tehran: the Big Three (USSR, Britain, and US) agreed on the invasion of Nazi-occupied France over the objections of Churchill, who desired a Mediterranean-based invasion that would give Britain spheres of influence in Eastern Europe following the war’s conclusion (this decision would lead to the creation of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War); a United Nations Organization was tentatively agreed to; the USSR pledged to support the Pacific Theater campaign after Hitler was defeated
- Yalta: the three powers agreed to divide Germany into four occupation zones; tensions arose when discussing the future of Eastern Europe as the Western powers foresaw the development of tensions with the USSR; it was confirmed that a United Nations would be created; Roosevelt pressed Stalin for support in its war against Japan
- Potsdam: the only conference to take place after the war’s conclusion; Truman replaced Roosevelt as the US representative, and Clement Attlee replaced Churchill; Russian forces occupied most of eastern Germany, so it was agreed that the USSR could take over much of eastern Poland; Germany was divided pending a final peace treaty (which would be signed more than 40 years later); treaties were hammered out for Germany’s allies, but the USSR and the US signed separate treaties with Japan
- The stage was set by these three conferences for “decolonization” and the confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union

Partition of Germany - D. Holter
After Germany's defeat in World War II, the Allies and the Soviet Union divided its territory into controlled zones, as well as returning captured lands to their original owners. Germany was half occupied by Britain, France, and the US, and half occupied by the Soviet Union, with Berlin being split up in a similar fashion, despite being inside the Soviet zone.
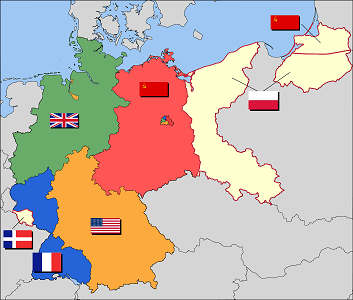
- Soviet forces kept a tight watch on border control and German emigration.
- The Berlin Wall was built to further divide Germany.
- Allied Berlin was surrounded on all sides by Soviets.
- Germany was officially reuinified on October 3, 1990.
Division of Europe/Iron Curtain Speech - Jordan Hubbard
· The Iron Curtain was a symbolic, ideological, and physical boundary dividing Europe after the end of WWII in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991.
· The Iron Curtain divided Europe into East and West.
· Eastern Europe consisted of the Soviet Union which annexed Eastern Poland, Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania, part of eastern Finland, northern Romania. The Soviet Union made East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania, and Albania satellite states.
· The communist Eastern Bloc had military and economic alliances such as COMECON and the Warsaw pact while Western Europe had NATO.
· Winston Churchill popularized the phrase “iron curtain” in his “Sinews of Peace” speech at Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri on March 5, 1946.
· A famous quote from his speech is, “from Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent."
· "Iron Curtain." Wikipedia. 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron_Curtain>.

This is a political cartoon of Winston Churchill looking under the Iron Curtain.
United Nations (1950s) – Andrew Steiner
- The idea to create a United Nations organization was confirmed at the Yalta Conference, the last of the wartime conferences between the US, Britain, and the USSR
- The goal of this new organization was to be more representative of the world’s peoples and create a more lasting peace without the blatant disregard for the losers that existed in the Treaty of Versailles
- 51 countries were original members of this body, either by actively fighting against the Axis powers or by signing declarations of alliances with the Allied Nations towards the beginning of 1945
- The US, Britain, France, USSR, and China comprised the UN Security Council’s permanent nations; each retained a veto power to maintain control over UN actions and moderate the intentions of opposing factions (i.e. the US and the Soviet Union during the Cold War would veto policies overly favorable to the other)
- Has helped to reduce violent conflict and provide refugee relief around the world
- Has sponsored conferences critical to shaping policies affecting child labor, women’s rights, and environmental protection

The United Nations headquarters on the East River in New York City.
"History of the United Nations." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.. 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_United_Nations>.
Stearns, Adas, Schwartz, and Gilbert, World Civilizations: The Global Experience. 4th. Pearson Education, Inc., 2005.
Berlin Blockade and Airlift – Cameron Tripp
- The USSR was afraid of a strong Germany
- They had been invaded by Germany twice
- They blocked off all land and rail routes into West Berlin
- People had to rely on stored food or else starve to death
- The Soviets thought the plan was working
- The Western powers began an enormous airlift effort
- They brought 5,000 tons of supplies a day
- The plan backfired in three ways:
- It made the West wary of the USSR
- It accelerated the Allied powers plans for an independent West Germany
- It helped create NATO, an American-Western European Military Alliance
"Berlin Blockade." PBS. PBS. 4 Apr 2009 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/bomb/peopleevents/pandeAMEX49.html.

The Berlin Airlift saved many people from dying of starvation,
Truman Doctrine -Rebecca Overcash
- The Truman Doctrine arose from a speech delivered by President Truman before a joint session of Congress on March 12, 1947.
- President Harry S. Truman established that the United States would provide political, military and economic assistance to all democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces.
- The immediate cause for the speech was a recent announcement by the British Government that it would no longer provide military and economic assistance to the Greek Government in its civil war against the Greek Communist Party.
- Because of this, Truman felt like it was the United States duty to defend and help out nations that needed it.
- Truman asked for $400,000,000 for this aid program, mostly for Greece and Turkey.

President Truman delivering his speech later known as the Truman Doctrine.
"The Truman Doctrine, 1947." U.S. Department of State. 13 Apr 2009
<http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ho/time/cwr/82210.htm>.
"Truman Doctrine." spartacus. 14 Apr 2009
<http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/USAtrumanD.htm>.
"Origins of the Cold War, 1945-1953." ccccd. 14 Apr 2009
<http://iws.ccccd.edu/kwilkison/online1302home/20th%20Century/ColdWar.html>.
Marshall Plan -
Marshall Plan- JC Bunch
The Marshall Plan was the primary plan of the United States for rebuilding and creating a stronger foundation for the countries of Western Europe, and repelling communism after World War II. The initiative was named for Secretary of state George Marshall and was largely the creation of State Department officials, especially William L. Clayton and George F. Kenna

George Marshall
NATO and Warsaw Pact - Taylor McAlister
-NATO
- stands for North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- was formed in 1949 under the leadership of the U.S.
- if one was attacked, all in NATO would defend it
- purpose was to group most Western European powers and Canada in a defensive alliance against possible USSR aggression.
- used to rearm West Germany for resisitance to communism
- also allowed the placing of U.S. military in NATO nations and West Germany
- was leading forces in Korean War and Vietnam War
- Members: U.S., Canada, Great Britian, France, Belgium, Netherlands, Norway, Italy, Turkey, Greece, West Germany, and others small countries
- Is still around to this day
-Warsaw Pact
- the response to the NATO alliance
- Soviet Union formed this among its Eastern European countries
- signed together in Warsaw, Poland in 1955
- if one country was attacked, all would help it
- consisted of Albania (withdrew in 1961, formally in 1968), Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, East Germany, Poland (of course), Romania, and the USSR
- dissolved in 1991 at the last meeting in Prague

This represents the countries that were in the NATO and Warsaw Pact alliances. NATO=blue. Warsaw Pact=red.
"Warsaw Pact." Wikipedia 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warsaw_Pact>.
Containment Policy and Domino Theory- Toomey
· The “containment” notion was born off of the Domino Theory
· The Domino Theory consisted of the belief that if one country became communist, the surrounding ones would too.
· containment defined the Truman Doctrine
· American intervention in the Greek Civil War resulted in the Truman Doctrine, the policy of aiding nations defending themselves against communist forces.
· What became known as the Domino Theory was soon created.
· Congress was persuaded to accept responsibility for supporting countries under communist pressure, i.e. containment.

President Harry Truman
"The Domino Theory." Travel & History. 2 Apr 2009 <http://www.u-s-
history.com/pages/h1965.html>.
Korean War (basic, broad overview) - Evan Hoke
- The Korean War was a conflict between Communist and non-communist forces in Korea from June 25, 1950 to July 27, 1953.
- This conflict took place from June 25, 1950 to July 27, 1953.
- Korea was divided at the 38th parallel into Soviet (North Korean) and U.S. (South Korean) zones of occupation at the end of WWII.
- Rival governments were established in 1948.
- The Republic of Korea was proclaimed in the South and the People's Democratic Republic of Korea in the North.
- The Korean War did prove to be a long and bloody war, though it did not escalate into a world war.
- The greatest burden of the war fell on the shoulders of the United States.

Photos of the Korean War Veterans Memorial.
Photo: "12 Monuments Dedicated to Death and Destruction: From War Memorials to Military Sculptures." 08 MAY 2008 6 Apr 2009.
Info: "Korean War - 1950-53." (1998) 6 Apr 2009.
Vietnam War (basic, broad overview) - Will Boggs
- The Vietnam War has many different names depending on your location. Some parts of the world refer to the Vietnam War as the Second IndoChina War. However the people in Vietnam call the war the American War.
- The war occurred in Laos and Cambodia from 1955 to 1975.
- The war was between North Vietnam supported by its communist allies and South Vietnam
which was supported by the United States and members of the SEATO.
- The Vietcong, the forces of South Vietnam, fought a largely guerilla warfare tactics style. They also relied mainly on the superior air power.
- The North Vietnam army fought a more conventional war style dedicating many troops to its attacks.
- The reason that the United States entered the war was to continue its plan of containment. THey did not want communist forces to take over South Korea.
- In January 1973 there was a treaty signed however fighting still existed. Eventually in 1975 North Korea captured Saigon and this reunited South and North Korea.
- In the Vietnam war between 3 to 4 million Vietnamese people were killed, 1.5 to 2 million Laotians and Cambodians, and 58,189 United States soldiers.
 This is a South Vietnamese air force. The South Vietnamese relied heavily on their aerial dominance in this war.
This is a South Vietnamese air force. The South Vietnamese relied heavily on their aerial dominance in this war.
"Vietnam War." Wikipedia. 1 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vietnam_War>.
Niikita Khrushchev - Adam Barr
- Born in Kaliknovka on April 15, 1894 to peasant parents
- Served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964, following the death of Josef Stalin
- Helped facilitate the “de-Stalinization” of the Soviet Union and inspired a few liberal reforms in agriculture and foreign policy
- In 1961, he approved the plans for the Berlin wall, and construction began later the same year
- He was resigned from office in 1964
- Khrushchev died on September 11, 1971 of a heart attack
 A photograph of Nikita Khrushchev in his uniform. He looks kind of goofy.
A photograph of Nikita Khrushchev in his uniform. He looks kind of goofy.
"Nikita Khrushchev." Wikipedia. 1 Apr 2009. 1 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nikita_Krushchev>.
Nuclear Arms Race (basic, broad overview) -
MAD and deterrence -
Soviet Invasion of Hungary-Abby Pardue
Suez Crisis -
Suez Crisis – R Stewart
· Began July 26, 1956 when Egyptian President, Gamal Abdel Nasser, decided to nationalize the Suez Canal
· France and Britain planned to intervene, while Israel planned an invasion of Egypt
· Against the urging of US President Eisenhower, Israel proceeded to attack Egypt on Oct. 29
· Britain and France mobilized their forces with intentions of occupation, demanding that Egypt and Israel move their forces at least 10 miles from the Canal
· British and French forces began attacking Egypt with air raids on October 31
· To this point, the United States had mobilized three attack carries and was primarily concerned with the safe evacuation of US nationals from the area
· On November 5th, the Soviet Union became involved saying that they would use whatever force necessary to maintain peace
· On November 6th, British and French force agreed to a cease-fire
· Tensions between the US and Soviets remained high until UN forces provided a buffer for the Egyptians

The Suez Canal is stategically important because it connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, negating the need to round the southern tip of Africa
Pike, John. "Suez Crisis." GlobalSecurity.org. 27 APR 2005. GlobalSecurity.org. 31 Mar 2009 http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/ops/suez.htm.
Bay of Pigs Invasion - Maggie Dillon
- Unsuccessful attempt by a group of US-trained exiles to invade Cuba
- aim was to overthrow Cuban government ruled by Fidel Castro
- planned and funded by the US
- Launched in April 17 1961
- Cuban forces consisted of militia and armed civilian fighters
-Trained by "eastern bloc" nations (Soviet controlled)
- Cuban forces defeated the invading forces in a mere 3 days
- caused a rapid deteriation of Cuban-American relations
- followed up by the Cuban Missile Crisis the next year
- 
Location of the Bay of Pigs
Berlin Wall- L.Ross
-Built on August 13, 1961
-Divided West Berlin (democratic) and East Berlin (Communist)
-West Berlin was run by the Americans, British, and French and East Berlin was run by the Soviet Union
-96 mi barbed wire barricade and concrete wall with an average height of 11.8 ft
-Three checkpoints: Alpha, Bravo, and Charlie
-Main function of the checkpoint was to register and inform members of the Western Military Forces before entering East Berlin
-Mass demonstrations against the government in East Germany began at the end of September until November 1989
-At 10:30 pm November 9, 1989 at the Bornholmer Strasse, East Berliners demanded passageway and it was granted, ending the Berlin Wall and the separation of East and West Berlin
-Pieces of the Wall remain still remain though only for historical reasons
 On the East side of the Berlin Wall people were not able to get up close to the wall but on the West, as you can see, Berliners took great joy in spray painting the Wall.
On the East side of the Berlin Wall people were not able to get up close to the wall but on the West, as you can see, Berliners took great joy in spray painting the Wall.
Dailysoft: IT-Consulting, Photography, Berlin and Berlin Wall information. 14 Apr. 2009 <http://www.dailysoft.com/berlinwall/>.
Cuban Missile Crisis - Meghan Edwards
-confrontation between United States, Soviet Union, and Cuba in early 1960s
-also referred to as "Carribbean Crisis" and "October Crisis"
-Khrushev (Soviet Union) placed military missiles in Cuba.
-Kennedy's response was to set up a naval blockade and have Khrushev remove the missiles.
-United States feared Soviet communisitc expansion into Cuba
-"Operation Mongoose" was a series of covert operations against Castro's government
-this is the closest that the world has ever come to nuclear war

http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_3cib3fK139M/SXr52sPSyuI/AAAAAAAAAkM/4NGKCMaKwkk/s400/Cuban+Missile+Crisis+Sattelite+Photo.jpg
"An overview of the Crisis." Cuban Missile Crisis 31 Mar 2009 <http://library.thinkquest.org/11046/days/index.html>.
Prague Spring and the Soviet Invasion of Czechoslovakia -
Brezhnev Doctrine - John Caudle
- Soviet foreign policy to justify their invasion of Czechoslovakia
- It went against some earlier Soviet military expeditions
- The policy uplifted socialist efforts and condemned capitalist ones
- They hoped to maintain the eastern bloc as a buffer from the West
- Preserve the Warsaw Pact so that the Soviet Union would be supported by other communist regions
- This policy designated the rights of the Soviet Union to define communism and socialism and to uphold them
- Treaties followed the passage of the policy to ensure Soviet communist power over other communist states
 This is a map of what the Brezhnev Doctrine justified for the Soviet Union. They used over 500,000 troops when invading Czechoslovakia.
This is a map of what the Brezhnev Doctrine justified for the Soviet Union. They used over 500,000 troops when invading Czechoslovakia.
Halsall, Paul. "Modern History Book: The Brezhnev Doctrine, 1968." 1997. Fordham. 1 Apr 2009 <http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/mod/1968brezhnev.html>.
Wilde, Robert. "Brezhnev Doctrine." About.com. 2008. About.com. 1 Apr 2009 <http://europeanhistory.about.com/od/glossary/g/glbrezhnevdoct.htm>
Sino-Soviet Split - Colt Burgin
- 1963
- Rift developed between China and the USSR
- Alliance bewtween countries was broken
- China and USSR were considered 2 communist countries that were very strong partners in the Cold War so split was very surprising.
- Caused by the amount of tension between the two countries. Also because of differences.
- Caused major change in war
- Made it possible for limited nuclear test ban treaty
- effectedwhole world not just the two countries.

The leaders of China and The USSR, the countries of the Sino Soviet Split.
Citation-
"The Sino-Soviet Split." MSN Encarta. Microsoft. 2 Apr 2009 <http://encarta.msn.com/sidebar_461575482/The_Sino-Soviet_Split.html>.
Detente - Dalyn Bellingham
- French term meaning " the relaxation of strained relations or tensions"
- Applied to international situations where previously hostile nations not involved in an open war relax tensions through diplomacy and policies
- Generally refers to the de-escalation of hostility between the Soviet Union and United States and the closing of the Cold War from 1960s to 1980s
Reasons for Relaxing Tensions
- Soviet leadership felt that the economic burden of the nuclear arms race was too much
- America was facing economic trouble through their involvement in Vietnam and Lyndon Johnson sought to improve the government welfare state

Reagan and Gorbachev meeting in 1985
"Cold War." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 29 Mar 2009, 23:23 UTC. 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cold_War&oldid=280524939>.
"Détente." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 18 Mar 2009, 06:51 UTC. 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=D%C3%A9tente&oldid=278051780>.
Afghan War - Josh Broach
The Soviet conflict in Afghanistan was sparked when the Soviet’s invaded supporting the Marxist
People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan.
Inside of Afghanistan the
mujahideen rebels were supported by several Muslim nations and the United States.
Occupation by the Soviets began in 1979 with the occupation of Kabul and major urban centers. Their objective was to remove the rebels from the country and establish the communist government as dominant.
The CIA and Jimmy Carter had undergone the secret signing of operations to traffic in weapons to the communist fighters.
Mainly Guerilla warfare ensued and the terrain, foreign assistance, and shear size of the country made it impossible for the Soviets to tame all corners of the nation.
Operation Cyclone, the funding by the US to Pakistan to fight the Soviets was a total success as other nations including the UK and the PRC contributed greatly to the war effort, over a billion dollars a year was supplied to the fighters from all foreign nations considered.
Around 1987 the Soviets had been defeated in almost every aspect that they began the withdrawal. Overall it was peaceful because they came to terms with local mujahideen who allowed them safe passage back home by 1989.
The end of the war signaled the end of détente and the Geneva Accords guaranteed total soviet withdrawal and the peace in Pakistan and Afghanistan.
The government however still laid in ruin as there was still civil strike between the two original groups.
The war was commonly compared to the United State's Vietnam because a much smaller and less resourcesful nation dominated a superpower.

"Soviet war in Afghanistan." Wikipedia. Wikipedia. 6 Apr 2009.
Soviet modernization and industrialization of Eastern Europe -
Andrei Sakharov, Alexander Sozhenitsyn, and the Soviet dissident movement -
Lech Walesa and Solidarity - Kim Martinez
Lech Walesa – Polish politician & co-founder of Solidarity
· Worked as electrical technician
· 1980 - Led occupational strike of 17,000 shipbuilders at Gdansk Shipyard – this constituted foundation of Solidarity
· Solidarity was 1st non-communist trade union in a communist country
o Advocated non-violence
o The strike & subsequent Solidarity led to imposition of martial law as an attempt of the communist government to crush political opposition against communist control in Poland – Walesa was arrested and imprisoned 11 months
o Ideas of Solidarity spread throughout Poland and Eastern block countries – influenced strengthening of anti-communist ideals and movements, which in turn caused weakening of communist governments and ultimately contributed to the collapse of the Soviet Union
· 1983 – Walesa awarded Nobel Peace Prize
· 1989 – Walesa awarded Presidential Medal of Freedom
· 1990 – 1995 – Walesa served as President of Poland
 Lech Walesa with world leaders
Lech Walesa with world leaders
"Lech Walesa ." Wikipedia. Wikipedia. 3 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lech_Wa%C5%82%C4%99sa>.
Gorbachev, perestroika, glasnost -
Collapse of the Soviet Union (basic, broad overview) - Andrew Craver
 Started collapsing in 1985
Started collapsing in 1985
 There were many failed attempts at reform due to people being unsatisfied with the government, but the government was still too strong for the people to overturn.
There were many failed attempts at reform due to people being unsatisfied with the government, but the government was still too strong for the people to overturn.
 SU was likely spread too thin. The government was no longer capable of providing their people with the proper day-to-day needs.
SU was likely spread too thin. The government was no longer capable of providing their people with the proper day-to-day needs.
 Finally after finally, realizing they had lost power, the Communist power gave up control on 07 February 1990.
Finally after finally, realizing they had lost power, the Communist power gave up control on 07 February 1990.
 15 SSR republics held there first elections over the next few weeks.
15 SSR republics held there first elections over the next few weeks.
 After this the SU slowly began to deteriorate, eventually falling into failure by 31 December 1991. (All Communist Soviet Union officials were removed by this date)
After this the SU slowly began to deteriorate, eventually falling into failure by 31 December 1991. (All Communist Soviet Union officials were removed by this date)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collapse_of_Soviet_Union
ending it
 http://images.ask.com/fr?q=USSR+Collapse&desturi=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.azer.com%2Faiweb%2Fcategories%2Fmagazine%2F43_folder%2F43_articles%2F43_poster.html&fm=i&ac=13&ftURI=http%3A%2F%2Fimages.ask.com%2Ffr%3Fq%3DUSSR%2BCollapse%26desturi%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.azer.com%252Faiweb%252Fcategories%252Fmagazine%252F43_folder%252F43_articles%252F43_poster.html%26imagesrc%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.azer.com%252Faiweb%252Fcategories%252Fmagazine%252F43_folder%252F43_photos%252F43_poster4.jpg%26thumbsrc%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fimgtn2.ask.com%252Fts%253Ft%253D772551172621650249%2526pid%253D23296%2526ppid%253D6%26o%3D0%26l%3Ddir%26initialURL%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.ask.com%252Fpictures%253Fl%253Ddir%2526o%253D0%2526q%253DUSSR%252520Collapse%2526qsrc%253D0%2526qid%253D63ECFB10FB323ABE12E077DBDC70FC26%2526pstart%253D18%2526page%253D2%26thumbuselocalisedstatic%3Dfalse%26fn%3D43_poster4.jpg%26imagewidth%3D147%26imageheight%3D216%26fs%3D23%26ft%3Djpg%26f%3D2%26fm%3Di%26ftbURI%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.ask.com%252Fpictures%253Fq%253DUSSR%252BCollapse%2526page%253D2%2526o%253D0%2526l%253Ddir%2526pstart%253D18&qt=0
http://images.ask.com/fr?q=USSR+Collapse&desturi=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.azer.com%2Faiweb%2Fcategories%2Fmagazine%2F43_folder%2F43_articles%2F43_poster.html&fm=i&ac=13&ftURI=http%3A%2F%2Fimages.ask.com%2Ffr%3Fq%3DUSSR%2BCollapse%26desturi%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.azer.com%252Faiweb%252Fcategories%252Fmagazine%252F43_folder%252F43_articles%252F43_poster.html%26imagesrc%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.azer.com%252Faiweb%252Fcategories%252Fmagazine%252F43_folder%252F43_photos%252F43_poster4.jpg%26thumbsrc%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fimgtn2.ask.com%252Fts%253Ft%253D772551172621650249%2526pid%253D23296%2526ppid%253D6%26o%3D0%26l%3Ddir%26initialURL%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.ask.com%252Fpictures%253Fl%253Ddir%2526o%253D0%2526q%253DUSSR%252520Collapse%2526qsrc%253D0%2526qid%253D63ECFB10FB323ABE12E077DBDC70FC26%2526pstart%253D18%2526page%253D2%26thumbuselocalisedstatic%3Dfalse%26fn%3D43_poster4.jpg%26imagewidth%3D147%26imageheight%3D216%26fs%3D23%26ft%3Djpg%26f%3D2%26fm%3Di%26ftbURI%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252Fwww.ask.com%252Fpictures%253Fq%253DUSSR%252BCollapse%2526page%253D2%2526o%253D0%2526l%253Ddir%2526pstart%253D18&qt=0
*****EXTRA CREDIT opportunity**: There are more terms/concepts this week than students in the class. I need your help completing the extra terms/concepts. You can claim ONE additional term/concept to complete - it's first come, first serve. You will receive up to 25 extra credit points towards this assignment (classwork/homework category) for the extra effort.
Extra Credit IDs:
Chernobyl accident - Maggie Dillon
- April 26, 1986, Ukraine, then part of the USSR
- Considered worst Nuclear power plant disaster in history
- USSR didn't admit the accident until nuclear alarms detected the radiation were set off in SWEDEN
- Reactory #4 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power plant exploded
- Only 2 people died from the actual explosion, but the cloud sent out a massive amount of radioactive fallout
- over 400 times as much as the atomic bomb on Hiroshima released
-reactor 4 suffered a massive power excursion, resulting in a steam explosion, that tore the top from the reactor, and dispersed large amounts of radioactive particulate and gaseous debris mostly Cesium-137 and Strontium-90
- World Health Organization attributed 56 direct deaths and estimated that there may be 4,000 extra cancer deaths
- light nuclear rain fell as far away as Ireland
- resulting in the evacuation and resettlement of over 336,000 people
- City near Chernobyl called Pripyat was also evacuated
- certain limited areas remain off limits, the majority of affected areas are now considered safe for settlement and economic activity
This map shows the radiation zones surrounding the Plant

Welfare State - John Caudle
- Supported by the consolidation of democracy
- Basic premise of the modern welfare state established in Western Europe by 1948
- Variety of government programs to help people after World War II
- The U.S. soon followed by adding welfare measures to President Johnson’s programs
- Assist the poor and elderly
- Helped with medical care and insurance programs
- Britain nationalized healthcare after the welfare state was established
- Increased contacts between government and citizens
- The welfare state provided great help for those in need, but was also as a great expense
- It channeled tax money to different areas and enlarged the bureaucracy
- Although countries use a welfare program it took many years to develop a system to stabilize the monetary issues it involves
 Poster showing the need for a welfare system in the mid 1900s.
Poster showing the need for a welfare system in the mid 1900s.
Green Movement - Taylor McAlister
- a movement that supported the ideas of green politics
- political ideology that supported ecological and environmental goals
- achieveing goals through a grassroots movement and participatory democracy
- name coined by die Grünen, first successful green Party, in 1970s.
- share many ideas of ecology, conservation, enviromental, feminism, and peace movements
- was a nonviolent movement
- many different perspectives of Green Movement
- Left- Eco-socialism, an ideology that combines ecology, environmentalism, socialism and Marxism
- more follow the geo-libertarian views that emphasize natural capitalism- a book about the economy and how it would be with an economy of natural resources and ecosystem services that sustain us

A picture of what the Green Movement was fighting for, a better world with the economy that is environmentally friendly
"A Brief History of the Modern Green Movement." WebEcoist 2008 2 Apr 2009 <http://webecoist.com/2008/08/17/a-brief-history-of-the-modern-green-movement/>
European Union - Kim Martinez
· economic and political union of 27 member states (currently – three are candidates for admission)
· Began in 1993 as a predecessor to European Coal & Steel Community and European Economic Commission – these prior two organizations were started after WWII as a move toward European integration and an effort to block future imperialistic aims of countries
· Motto: “ United in Diversity” and Anthem: “Ode to Joy” by Beethoven
· European Union has developed a single market with standardized laws – freedom of movement of people, goods, services & capitals throughout its domain
· Has developed common policies on trade and regional development
· For a country to join EU, must adhere to Copenhagen Criteria
o Have stable democracy which represents human rights & rule of law
o Have functioning market economy
o Accept EU laws and guidelines
· 16 of the member states use common currency (Euro)
· EU made of 500 million citizens
· EU comprises 30% of Gross World Product
 The European Union Flag
The European Union Flag
"European Union." Wikipedia. Wikipedia. 2 Apr 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Union>.
New Feminism -
Popular Culture(western - look at pages 796-99) - Andrew Craver
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.